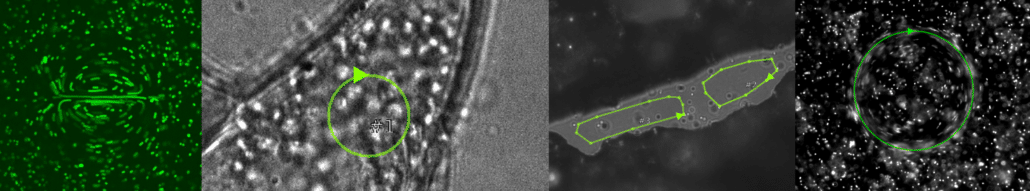
FLUCS
Micro flow photomanipulation
With FLUCS photomanipulation, the non-invasive and flexible control of microscopic flows, we offer the microscopist a completely new tool to manipulate the sample. Active transport by fluid flows is a hallmark of many living microscopic systems, and the ability to actively control intracellular motion can add an entirely new dimension to life science research.
Read about FLUCS photomanipulation in this online article in Imaging and Microscopy.
Cooperation
The FLUCS photomanipulation system for microscopic flows has been developed based on a close scientific cooperation with Moritz Kreysing and his research group at the Max-Planck-Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics (MPI-CBG) in Dresden, Germany. Patents pending.
Thermo-viscous flow
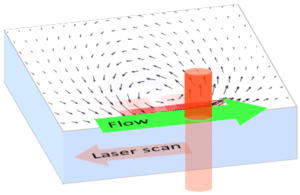
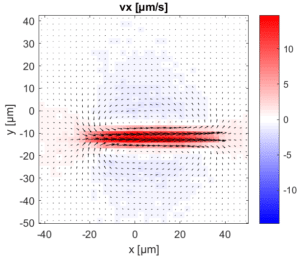
By moderately heating the specimen with a rapidly scanned infrared laser spot, directed fluid flows are induced. By flexibly designing the scan path of the laser, fluid is pumped along prespecified paths in the focal plane of a microscope. For optimal performance in aqueous solutions, the wave length of the IR laser is optimized for the absorption spectrum of water.
Flow specifications
| Variable | Unit | Min | Typical | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow velocity U | µm/s | 0 | 10 | 100 |
| Specimen thickness d | µm | 5 | 30 | 200 |
| Temperature increase ΔT | K | 0 | 5 | 50 |
| Spatial extent of flow pattern L | µm | 5 | 30 | 200 |
| Variable | Unit | Min | Typical | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow velocity U | “µm/s” | 0 | 10 | 100 |
| Specimen thickness d | µm | 5 | 30 | 200 |
| Temperature increase ΔT | K | 0 | 5 | 50 |
| Spatial extent of flow pattern L | µm | 5 | 30 | 200 |
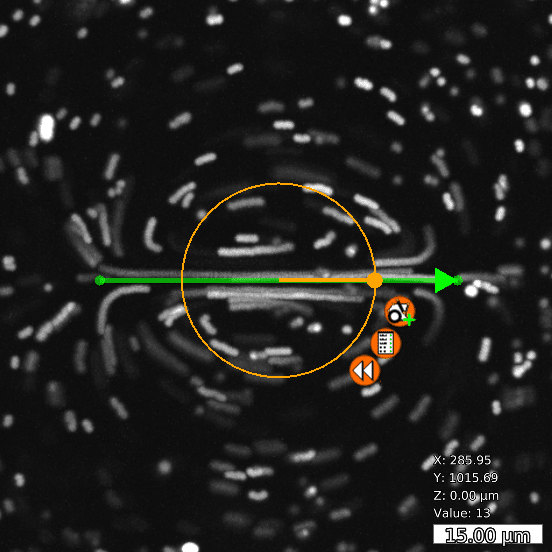
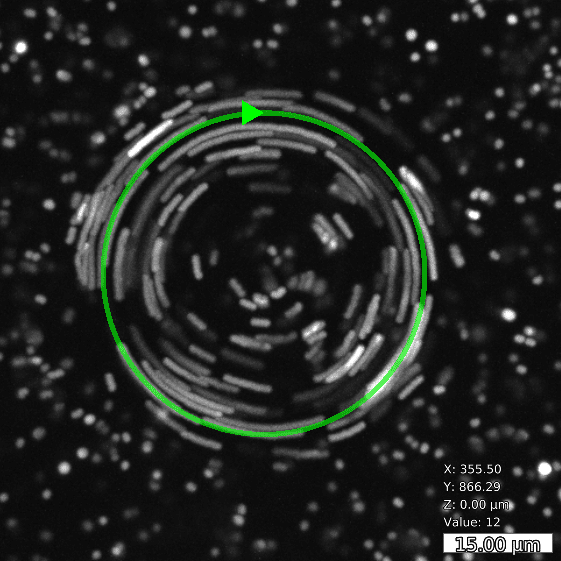
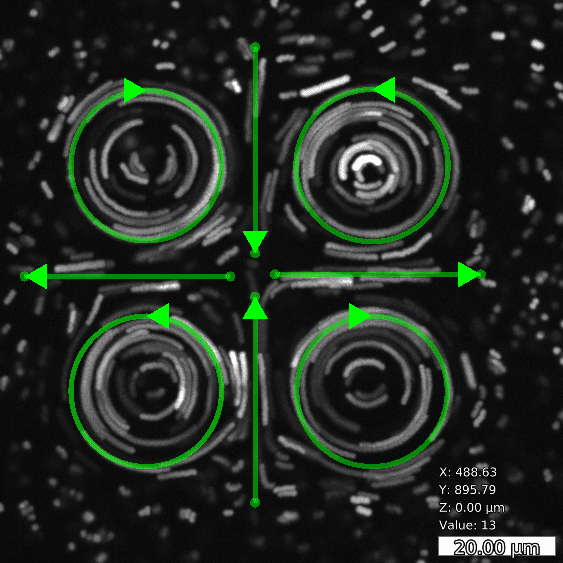
Basic and compound flow patterns
Flow patterns are directly defined in the current camera image. The speed of the flow is controlled by adjusting laser power and scan frequency. Temporal control has microsecond accuracy and can be embedded in complex experimental protocols.
Applications
Cell biology
- Cytoplasmatic streaming: Invert PAR domains in c. elegans embryo
- Local rheology measurement in cell
- Probe material properties of centrosomes with flow perturbations
- Hydrodynamic trapping and force measurement
- Localized temperature gradients
Biophysics
- Intra-cellular transport through advective micro flows, reaction-advection-diffusion systems
- Hydrodynamic trapping of cells, colloids, or particles
Microfluidics
- Flow pumping in micro channels
- Efficient micro-mixer, time-dependent flow
- Droplet based micro fluidics
- Sorting and selecting of colloids, cells or droplets
Medical research
- Sorting and handling of individual cells
Videos
Cytoplasmatic streaming in Elodea cells
Microscale flows
REFERENCES
- Erben, Elena, Weida Liao, Antonio Minopoli, Nicola Maghelli, Eric Lauga, and Moritz Kreysing. 2024. “Opto-Fluidically Multiplexed Assembly and Micro-Robotics.” Light: Science & Applications 13(1):59. doi: 10.1038/s41377-024-01406-4.
- Seelbinder, Benjamin, Susan Wagner, Manavi Jain, Elena Erben, Sergei Klykov, Iliya Dimitrov Stoev, Venkat Raghavan Krishnaswamy, and Moritz Kreysing. 2024. “Probe-Free Optical Chromatin Deformation and Measurement of Differential Mechanical Properties in the Nucleus.” ELife 13:1–21. doi: 10.7554/eLife.76421.
- Liao, Weida, Elena Erben, Moritz Kreysing, and Eric Lauga. 2023. “Theoretical Model of Confined Thermoviscous Flows for Artificial Cytoplasmic Streaming.” Physical Review Fluids 8(3):034202. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevFluids.8.034202.
- Minopoli, Antonio, Susan Wagner, Elena Erben, Weida Liao, Iliya D. Stoev, Eric Lauga, and Moritz Kreysing. 2023. “ISO-FLUCS: Symmetrization of Optofluidic Manipulations in Quasi-Isothermal Micro-Environments.” ELight 3(1). doi: 10.1186/s43593-023-00049-z.
- Chartier, Nicolas T., Arghyadip Mukherjee, Julia Pfanzelter, Sebastian Fürthauer, Ben T. Larson, Anatol W. Fritsch, Rana Amini, Moritz Kreysing, Frank Jülicher, and Stephan W. Grill. 2021. “A Hydraulic Instability Drives the Cell Death Decision in the Nematode Germline.” Nature Physics 17(8):920–25. doi: 10.1038/s41567-021-01235-x.
- Erben, Elena, Benjamin Seelbinder, Iliya D. Stoev, Sergei Klykov, Nicola Maghelli, and Moritz Kreysing. 2021. “Feedback-Based Positioning and Diffusion Suppression of Particles via Optical Control of Thermoviscous Flows.” Optics Express 29(19):30272. doi: 10.1364/OE.432935.
- Stoev, Iliya D., Benjamin Seelbinder, Elena Erben, Nicola Maghelli, and Moritz Kreysing. 2021. “Highly Sensitive Force Measurements in an Optically Generated, Harmonic Hydrodynamic Trap.” ELight 1(1):1–9. doi: 10.1186/s43593-021-00007-7.
- Mittasch, Matthäus, Vanna M. Tran, Manolo U. Rios, Anatol W. Fritsch, Stephen J. Enos, Beatriz Ferreira Gomes, Alec Bond, Moritz Kreysing, and Jeffrey B. Woodruff. 2020. “Regulated Changes in Material Properties Underlie Centrosome Disassembly during Mitotic Exit.” Journal of Cell Biology 219(4). doi: 10.1083/JCB.201912036.
- Kreysing, Moritz. 2019. “Probing the Functional Role of Physical Motion in Development.” Developmental Cell 51(2):135–44. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2019.10.002.
- Mittasch, Matthäus, Peter Gross, Michael Nestler, Anatol W. Fritsch, Christiane Iserman, Mrityunjoy Kar, Matthias Munder, Axel Voigt, Simon Alberti, Stephan W. Grill, and Moritz Kreysing. 2018. “Non-Invasive Perturbations of Intracellular Flow Reveal Physical Principles of Cell Organization.” Nature Cell Biology 20(3):344–51. doi: 10.1038/s41556-017-0032-9.